Bitcoin critics like to ask why people don't all use Bitcoin as money if it is the better money. The answer is often that too few people know Bitcoin, let alone understand it. This is also true, but what is often left out of this discussion is that competition for money is suppressed by the state. As a rule, only a state's paper money is legal tender and is therefore highly privileged.
Legal tender
A legal tender is characterized by the fact that sellers are obliged by the state to accept it for payments or debt settlements. In the eurozone this is the euro, in the USA the US dollar and in Switzerland the Swiss franc. In addition, taxes and fees usually only have to be paid in the legal tender. In this way, the state forces people to demand state-controlled paper money.
Nowadays, state money is generally fiat currency, i.e. money monopolized by the state that can be created out of nothing and dematerialized.
Exceptions
However, there are some exceptions to this. For example, special gold coins are also legal tender. Often, however, only at their face value, which is significantly lower than the market value. In Germany, this is the "German gold euro" (approximately 14 grams) with a face value of 100 euros. However, the market value is over 1,000 euros, so paying with the coin would be a huge loss.
In addition, in several US states - including Wyoming, Arizona, Texas and Utah - certain gold and silver coins are legal tender at their current market value. In this case, however, this only means that the precious metals are exempt from VAT and no taxes are payable on realized gains. However, there is no obligation to accept them and taxes cannot be paid with the physical coins.
In Switzerland, however, taxes and fees can even be paid with Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies in the canton of Zug and the city of Lugano.
And then, of course, there is El Salvador, the first country in which Bitcoin is the legal tender alongside the US dollar. Merchants there are also obliged to accept Bitcoin if it is technically possible. However, this law is not enforced and every merchant is free to decide which legal tender they wish to accept. However, citizens can pay taxes and fees with Bitcoin at any time and, of course, there is no capital gains tax.
Of course, there are other exceptions, such as the Central African Republic, Madeira and Prospera. However, the examples listed should suffice for a brief overview and are intended to emphasize that alternative means of payment only rarely have the same status as paper money.
Money competition
If we had a free money market, then the best money would prevail. This was already the case before the global introduction of fiat money. Over a long period of time, gold prevailed over silver, copper or even shells, salt and stones.
Theoretically, of course, different monies could also exist in parallel. One would then be free to decide which money to accept and use for payments. For example, gold and silver were also used in parallel as money for a while. Around 1870, however, the gold standard became established worldwide. It is actually quite beneficial when mankind agrees on one money. You can pay with one money anywhere in the world.
What is (good) money?
Money is a very complex topic and there are different definitions. For example, it can be argued that currencies such as the euro and the US dollar are not real money. The euros that we have in our bank account are in fact only the liability of a bank:
Gold is money. Everything else is credit.
J. P. Morgan (1912)
A plausible definition is that of the representatives of the Austrian School of Economics: money is first and foremost simply a medium of exchange and consequently also a store of value and a unit of account. In addition, money is a good of its own class ("sui generis"). This means that more units of money are of no use to a society. Money is not a production or consumption good.
Money is also essential for a society based on the division of labor. This allows people to specialize, exchange their work for money and then become active on the market. In a barter system, on the other hand, if the hairdresser is hungry, he would have to find someone to prepare him a meal in return for a haircut.
Good money must fulfill several conditions: It must be homogeneous, durable, divisible, transportable/transferable, verifiable and scarce. However, you can add to this that money should be widely distributed and liquid. This is because money should be exchangeable at any time and always be in demand by people. The keyword here is network effect.
Scarcity
Gold has prevailed over other metals as money because it was scarcer. However, there are raw materials that are rarer than gold, such as rhodium. However, rhodium is directly consumed industrially and therefore the proportion of the new quantity to the existing quantity is always higher than for gold.
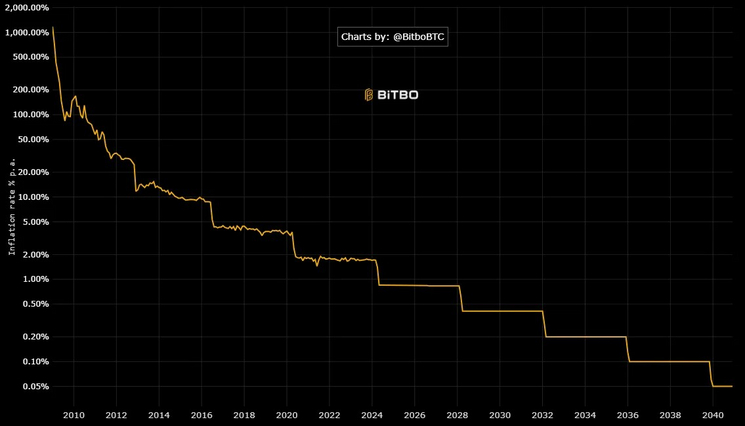
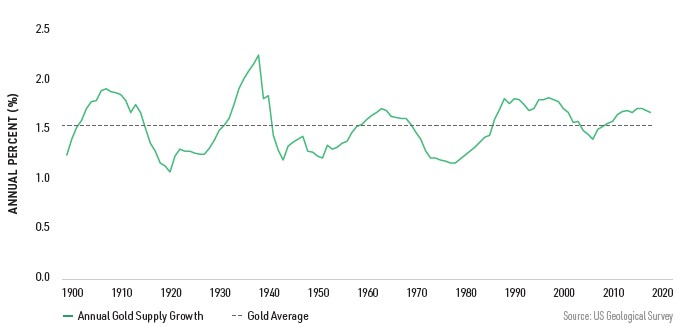
Scarcity can therefore be easily measured using the inflation rate of a currency, i.e. how much is added in a year as a percentage of the existing quantity. Alternatively, the "stock-to-flow ratio", which in the end is simply 100 divided by the inflation rate. At 0.85%, Bitcoin has had a lower inflation rate than gold for the first time since the 4th halving. In the past, gold's inflation rate was relatively stable at around 1.5 percent. Bitcoin is expected to ultimately have an inflation rate of 0% in 2140, as no more new Satoshis will be added.
By contrast, the US dollar, representative of the better fiat currencies, has expanded at a rate of just under 7% over the past decades. The weaker currencies, such as the Nigerian naira or the Venezuelan bolívar, have even expanded at significantly higher rates.
Money creation
Fiat currencies can be created out of nothing by central banks and authorized commercial banks. The extent to which the money supply changes is therefore at the discretion of monetary policy and also depends on how many new loans banks want to grant, meaning that fiat money is never really scarce.
Gold and Bitcoin can theoretically be found by anyone, but unlike fiat money, a service must be provided in return. The difference between gold and Bitcoin, however, is that the higher the equivalent value, the greater the increase in the quantity of gold. It then becomes more profitable to search for it and more cost-intensive. This ultimately results in more available gold, even if this is only possible to a limited extent. This is why the inflation rate of gold is also subject to quite strong fluctuations. With Bitcoin, on the other hand, it does not matter how much work is required to mine Bitcoin: The amount added is mathematically limited and the difficulty adjustment ensures that new units only come into circulation every ten minutes on average. We can therefore rule out that there will ever be more than the almost 21 million units.
In the case of gold, we also cannot know how much actually exists on this planet and how much can still be developed through meteorites or gold mining on other planets, for example. Furthermore, it cannot be completely ruled out that gold can be produced artificially at some point.
Counterfeit protection
With gold and fiat money, it is also quite difficult for normal people to determine whether it is not a counterfeit without the help of other means. Bitcoin, on the other hand, is completely forgery-proof. You can simply check the Bitcoin blockchain to see whether the promised amount of Bitcoin for the respective address is actually available for issue. The best way to do this is to operate your own Bitcoin Full Node. With this, you can keep the entire history of the Bitcoin blockchain yourself and really don't have to trust anyone.
Usability
Bitcoin is also ahead when it comes to transferability, as Bitcoin can be sent across the globe in its basic digital property in a few minutes. With Lightning, this is even possible in a matter of seconds and with almost zero fees. With gold, this would only be possible by means of certificates and therefore a central authority would have to be trusted. Fiat money is indeed easy to handle, but for transactions in distant countries, this form of money, or rather the banking system, reaches its limits. Apart from cash payments, we always have to trust a middleman. In fact, with digital fiat transactions, only information is exchanged and the real money is only sent between the banks in a bundle after a certain period of time. However, the consumer may not care about this for the time being.
With gold itself, it is also very costly to settle very small amounts. The smallest gold coin usually weighs 1/20 ounce and currently has an equivalent value of around 100 euros. In addition, the smaller the coin, the higher the surcharge for minting it. So if you don't want to fall back on certificate solutions, it can be difficult to buy gold in the supermarket.
One Bitcoin consists of 100 million Satoshis and one Satoshi currently has an equivalent value of around 0.0006 euro cents. This enables micro-transactions. As Bitcoin is digital, it would also be possible to divide a Bitcoin into even smaller units if required.
Bitcoin is also easier to transport than gold. Although a relatively large amount of value can be transported with a small amount of gold, the fact that gold is physical has disadvantages: With very large quantities, transportation becomes incredibly expensive and there is a risk of robbery. Bitcoin, on the other hand, can be transported anywhere free of charge and hidden. All you have to do is enter your private keyin your head, i.e. 12 or 24 words. For example, you can leave authoritarian regimes with a large fortune and access your Bitcoin again in another location. This is problematic with fiat money, however. Even when leaving the EU, citizens must declare a cash amount of over 10,000 euros. Carrying a large amount of cash always causes a stir and problems when crossing borders.
Resistance to censorship
Bitcoin is resistant to censorship due to its decentralized nature. So are fiat money and gold in their physical form, but digital transactions must always be trusted to intermediaries. Pressure can be exerted on these middlemen to censor. In fact, this is not uncommon. The disclosure platform WikiLeaks, for example, was blocked by PayPal in 2010 and then accepted donations via Bitcoin. Bank accounts can also be frozen or payment service providers can theoretically simply debit money as a penalty for spreading ''misinformation''.
All attempts at censorship have failed in the Bitcoin network. There are strong economic incentives for Bitcoin miners not to censor.
Homogeneity
Gold, Bitcoin and fiat money are homogeneous. This means that one unit of money always corresponds to another. 5 euros are always 5 euros, one gram of gold is always one gram of gold and one bitcoin is always one bitcoin. This would not be the case with land or real estate. Despite the same size, the location, for example, can justify a large difference in value.
Longevity
Good money must not decay over time or lose its physical properties. This would be the case with digital fiat money and Bitcoin. Gold is an extremely robust metal and fulfills this property quite well. We can see this from the fact that there are still gold coins that are hundreds of years old. Cash, on the other hand, is susceptible to fires or flooding. In addition, banknotes sometimes lose their validity and have to be exchanged for new ones.
Interim conclusion
Good money must be scarce. Gold and Bitcoin are not only scarcer, but also much fairer than the fiat money that is widely used around the world. However, Bitcoin is not only scarcer than gold, but also much better suited to a digitalized and globalized world. As gold is not well suited as a means of payment in its native form, it was also possible to finally abolish the gold standard in 1971. Bitcoin, on the other hand, could scale by means of "second layer technologies" such as the Lightning Network and thus be in no way inferior to fiat money in terms of usability.
So if you could choose freely, which money would you prefer to use? A money that can be multiplied at the push of a button or one that is physically or mathematically limited? You would probably feel more comfortable if the money you received in return for a service could not be produced by other people without it.
We would probably agree on the money that best fulfills the characteristics of good money and is also the most difficult to expand so that the money can maintain its value as well as possible.
Bitcoin vs. cryptocurrencies
At first glance, some of the advantages of Bitcoin listed above could also apply to other cryptocurrencies. However, Bitcoin clearly stands out here:
Bitcoin is the only truly decentralized and non-corruptible cryptocurrency. It is important to emphasize that no relevant cryptocurrency is even trying to compete at this level. Rather, the so-called altcoins are trying to be the better means of payment by allowing more transactions on the blockchain itself. However, this comes at the expense of decentralization and security, which are the cornerstones of trust without a state behind them. A larger number of transactions makes it virtually impossible for normal people to keep track of the transaction history themselves, so service providers have to be trusted.
Altcoins are therefore trying to become a means of payment without being suitable as a store of value or being able to compete with Bitcoin in this respect. However, for people to increasingly accept money voluntarily for payments, it must first have established itself as a store of value. Bitcoin is the cryptocurrency with the strongest network effect and the greatest market value.
Most people don't spend #Bitcoin till they have nothing else to spend. That's why the Medium Of Exchange adoption curve lags the Store Of Value adoption curve.
Cory Klippsten | Swan.com 🦢 #Bitcoin (@coryklippsten) November 17, 2021
By 2035 you'll be able to buy most goods and services in most places around the world denominated in sats. pic.twitter.com/pLThgheabe-
Bitcoin has perfected being a store of value and the blockchain serves as a security for this value. Second layer technologies then come into play for the function of the means of payment, allowing users to carry out unlimited, cheap and fast transactions. But not at the expense of Bitcoin's security, decentralization or scarcity.
Can Bitcoin be used as a means of payment?
Except in a few countries, such as China or Turkey, it is generally permitted to switch to Bitcoin for payment transactions. Although it is not mandatory for sellers to accept Bitcoin as a means of payment, it is generally not in the interests of freedom-loving people to accept it.
It is already possible to pay cheaply with Bitcoin in many places via the Lightning network. The fees are even significantly lower than for standard card payments. However, merchants generally exchange Bitcoin directly for fiat currency.
Nevertheless, payments with Bitcoin are a rarity. If you are not dependent on censorship resistance or privacy, then it makes perfect sense to save in Bitcoin and use the fiat money, which is losing value, for payments.
Disadvantages of alternative means of payment
Using alternative means of payment currently has a number of disadvantages.
By using an alternative currency, one generally hopes for an increase in value measured in fiat currency, at least in the longer term. However, it is a major disadvantage if taxes on profits are incurred on every transaction. Whether you exchange your Bitcoin into the respective currency beforehand or pay directly with it is irrelevant. In Germany, gains on gold and Bitcoin are tax-free after a holding period of one year. In the USA, there is no such holding period and taxes must always be paid on profits.
This can make it extremely complicated and costly to use Bitcoin as a means of payment. You have to record the exchange rate at the time of exchange and document the equivalent value and also when the Satoshis were acquired. Tools that can do this work for you are ''Cointracking'' for consumers and ''BTCPay Server'' for merchants.
If you use Bitcoin as a means of payment, you can drive adoption. On the one hand, it shows other people that Bitcoin can be used as money and on the other hand, the usability of the Lightning Network itself also benefits if there is more liquidity.
However, it is a huge problem when alternative means of payment are subject to VAT. In Germany, for example, the purchase of physical silver is subject to full VAT of 19 percent. This means that if you buy the equivalent of 1,000 euros, you will only receive 810 euros in silver. Silver would otherwise be relatively suitable for everyday cash payments, as a small coin (1/20 ounce) has the equivalent value of around one euro.
The exchange rates of alternative means of payment also fluctuate, measured in the currency that serves as the unit of account in the area. It is therefore also possible to suffer a significant loss of purchasing power over a certain period of time if you bet on Bitcoin or gold. For risk-averse people, this is therefore also a major mental challenge. However, the strong fluctuations of Bitcoin should not unsettle you.
Volatility is unavoidable on the path to monetization. By definition, a new money cannot go from zero to trillions without upward volatility. And with upside volatility comes speculators, leverage and periods of downside volatility follow.
Lyn Alden, renowned analyst
State education, economy and opinion-forming
There is hardly any awareness of the topic of money at school or university. In addition, the Austrian School of Economics tends to be a marginal phenomenon or even goes completely unmentioned, even in economics courses. Malicious tongues would claim that state educational institutions deliberately fail to educate students about our financial system so that the general public does not realize that our money can be created out of nothing. In the USA, almost 30 percent of the population still believe that the US dollar is backed by gold.
If people understood the monetary system, we would have a revolution before tomorrow morning.
Henry Ford, entrepreneur
Furthermore, most of the relevant economists are employed by the central banks themselves. Otherwise, they work at state universities or appear as experts in the state media. There are also simply some players who profit from the fiat money system.
In addition, the central banks themselves are deliberately trying to talk down alternatives such as Bitcoin:
One argument put forward by the European Central Bank (ECB) that Bitcoin is not money is that Bitcoin does not fulfill the function of a store of value. To refute this argument, it is worth taking a look at the development of Bitcoin's purchasing power compared to fiat currencies. The following charts are from the US central bank St. Louis and should actually illustrate the fluctuations of Bitcoin compared to the US dollar. However, if you extend the period under review, a clear picture emerges:
And the US dollar is still the stronger currency than the euro. So the fact that the ECB denies that Bitcoin is a store of value is obscene. Moreover, the ECB claims that Bitcoin is not a reliable medium of exchange. If this means that Bitcoin is not accepted everywhere as a means of payment, then the statement is understandable. From another perspective, however, nothing is as reliable as censorship-resistant Bitcoin transactions that no one can reverse. The statement that Bitcoin is not a unit of account is fundamentally true. Due to the strong fluctuations of Bitcoin, measured in goods, it is actually not yet well suited for pricing goods. However, this should change as it becomes more widespread.
The fact that central banks are turning against Bitcoin should come as no surprise. Bitcoin as the world's money could make central banks obsolete.
Nobody likes to saw at the branch they are sitting on. Fiat money gives states power and control. With a free money market, states would almost certainly not be able to exist in the (inflated) form in which they do today.
Outlook
As nobody likes to give up power voluntarily, it can be assumed that states will continue to try to suppress competitors. Especially if the competitive situation intensifies, for example if more and more people prefer Bitcoin to fiat currency. However, some politicians still see Bitcoin as competition that should not be taken seriously.
The state money monopoly with its many problems will probably be with us for many years to come.
There is less reason than ever to hope that states will become more trustworthy as long as the people have no choice but to use the money that the state makes available to them.
Friedrich August von Hayek, representative of the Austrian School and strong advocate of a free money market
The hope for a better world can remain, however, because we still have a choice. We can build on this:
A small step towards freer competition would be laws that would declare transactions with Bitcoin up to a certain amount irrelevant for tax purposes. There are also already efforts, for example in the US state of Texas, to introduce Bitcoin as a legal tender. The fact that high-ranking US politicians are campaigning for this shows that there are also influential forces that seem to be interested in a freer money market. The Bitcoin community in the USA has now become an interest group that should not be underestimated - and the trend is rising. For example, it can be decisive for electoral success if politicians position themselves positively towards Bitcoin. In fact, this can already be observed.
Game theory
Game theory is often used in this context. Roughly summarized, this is the assumption that states are virtually forced to allow Bitcoin so that they do not fall behind other states. In the event that Bitcoin ultimately establishes itself as the world's money, it is beneficial to be on board as early as possible. The whole industry around Bitcoin can also create local jobs and increase tax revenues. Or, like El Salvador for example, a country can also benefit economically from Bitcoin tourism. This could force other countries to follow suit.
Conclusion
Bitcoin is clearly superior to other forms of money and would presumably prevail in a free competition for money over time. For this to happen, however, Bitcoin must continue to establish itself as a store of value and become more widespread.
Even if it is not forbidden in principle to use alternative means of payment, the states set incentives to use their fiat money. This is particularly due to the fact that in most cases taxes are payable on price increases in alternative forms of money.
Free competition for money is a long way off, even if positive developments can be observed. It remains to be seen whether the states will try to put a stop to the further spread of Bitcoin. Attempting to do so would ultimately only show once again that Bitcoin cannot be banned.