Decentralized technologies or distributed ledger technologies are characterized by the fact that no central entity can exercise control in the network. Nevertheless, there are certain scenarios that can harm a blockchain or the network participants. One of these dangers is so-called "double spending attacks".
Imagine you go shopping and pay with a 50 euro bill. You then visit the store a second time and steal the same 50 euro bill.
Now you can pay with this bill a second time, even though you had already spent it originally. You can imagine a double-spending attack on a blockchain in a similar way.
Only it is much easier to create a counterfeit in the digital space. Whereas in the analog world, you need special paper, materials and equipment to create a good copy of a physical banknote, you can simply replicate digital data, as it ultimately only consists of bits.
You can imagine it like this: An attacker owns one Bitcoin. If he were to send this one Bitcoin several times to different parties, he would be cheating the network because he could only send this Bitcoin once (if it were not digital). Or hackers could simply copy coins from compromised transactions and pay them out themselves. We have visualized the scenario in the following diagram:
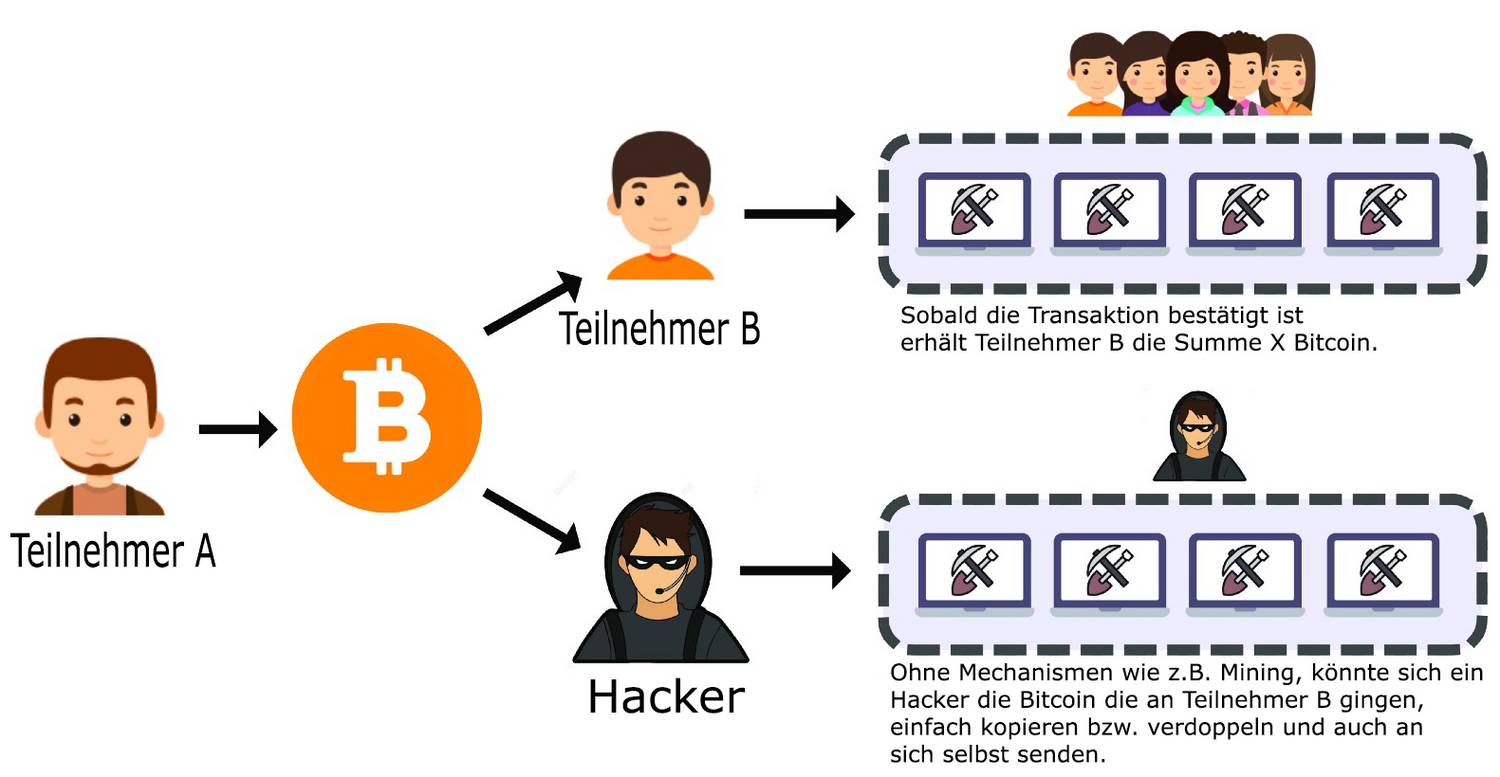
For this reason, the creation of digital money was a particular challenge. However, Satoshi ultimately succeeded in solving the problem of duplicate spending. The Bitcoin protocol does not allow data to be simply duplicated. Every Bitcoin is therefore unique. Nevertheless, the network must protect itself against an entity being able to spend a Bitcoin more than once.
To prevent bitcoins from being issued twice, the network checks whether this bitcoin has already been issued in the past. To do this, it must be ensured that the past data cannot be changed. Otherwise, the data can be manipulated in such a way that the network would recognize a double spend as valid.
One way of preventing attackers from simply changing the history of a blockchain is proof-of-work (PoW for short). This involves verifying blocks in a blockchain using a very energy-intensive process known as mining . If you want to change data in the past, at least as much energy must be expended as has flowed into the blockchain since this data was entered. This makes retroactive changes extremely unprofitable and extremely difficult. You can find out more about mining in the following Blocktrainer 1×1 article.
Another way to protect the past of a blockchain is through proof-of-stake (PoS for short). Here, the block producers are predefined by their stake. To get the chance to become a block producer, a lot of the internal currency must be spent. This makes double spending very expensive.